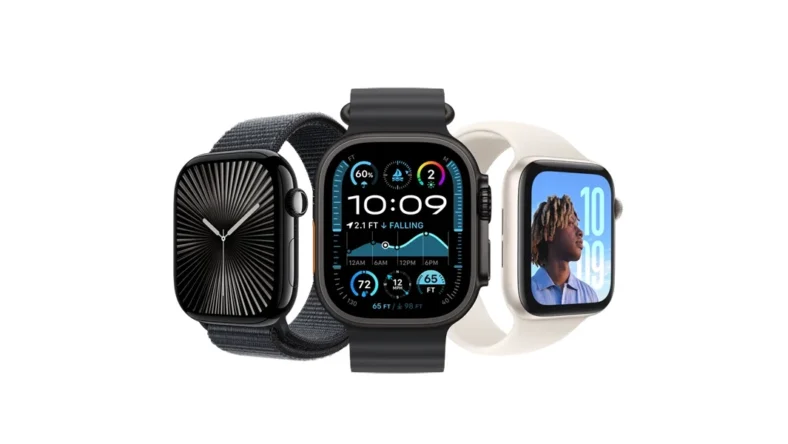
The past 10 years of the Apple Watch have marked the evolution of one of the world’s most important wearables
On April 24, 2015, Apple released the first-generation Apple Watch, entering a market that was still defining the world of smartwatches. Ten years later, the device has become one of the most widely used wearables in the world, with an estimated 100+ million active users globally.
The original Apple Watch focused primarily on notifications, basic fitness tracking and communication. Tim Cook introduced it in September 2014 as “the most personal device we’ve ever created.” The first model featured an optical heart rate sensor, which would be key to its future health offerings.
Apple’s progression in healthcare offerings has been consistent and focused on science. Series 1 and 2, released in 2016, added water resistance and built-in GPS. Series 3 (2017) introduced cellular connectivity, allowing the device to be a standalone device. With Series 4 in 2018, Apple implemented the FDA-cleared ECG app and fall detection, a shift toward healthcare capabilities.
The evolution continued with Series 5 (2019), which added an always-on display and compass. Series 6 (2020) introduced blood oxygen monitoring amid the COVID pandemic, while Series 7 (2021) featured a larger display and faster charging. The Series 8 (2022) added temperature sensing and car crash detection. Series 9 (2023) included the double tap gesture and more powerful on-device processing. Most recently, Series 10 (2024) introduced sleep apnea detection and consolidated health metrics in the new Vitals app.
Apple has focused on backing these features with scientific validation. The Apple Heart Study, launched in 2017 in collaboration with Stanford Medicine, enrolled over 400,000 participants, one of the largest studies of its kind, to evaluate the watch’s ability to identify atrial fibrillation. Subsequent research partnerships have included the Apple Women’s Health Study with Harvard and the Apple Hearing Study with the University of Michigan.
The Apple Watch’s fitness capabilities have expanded from the simple “Stand, Move, Exercise” rings to a comprehensive fitness ecosystem. The original Workout app supported just a handful of activities. Today’s version tracks over 90 different workout types with increasing sophistication. Swimming metrics now include stroke identification, pace and distance calculations. Runners can use features like ground contact time, vertical oscillation and running power. Other sports, such as tennis, basketball and skiing, have received dedicated tracking metrics. The watch provides recovery time recommendations, training load evaluations and cardio fitness level assessments for improved performance.
Apple Fitness+, launched in December 2020, offers guided workouts across 11 exercise types with real-time Apple Watch metrics displayed on-screen. The service has since grown to include meditation, post-pregnancy workouts and audio-guided outdoor walks featuring celebrity guests.
The Ultra line, first introduced in 2022, offers an extended battery life (up to 36 hours), improved GPS accuracy through dual-frequency support and features specifically designed for endurance athletes, hikers and divers.
Apple’s safety features have evolved from basic emergency calling to a sophisticated personal safety system. Fall detection uses accelerometer and gyroscope data to identify hard falls and automatically call emergency services if the user remains immobile. Emergency SOS enables quick access to emergency services worldwide, even on cellular models without an active plan.
In 2022, crash detection was added, capable of identifying severe car accidents and automatically alerting emergency responders. The Check In feature allows users to notify contacts when they’ve arrived safely at a destination. On Ultra models, a loud siren can help others locate the wearer in emergencies.
The physical design of the Apple Watch has evolved gradually. The original square-with-rounded-corners form factor remains, though cases have grown slightly larger (from 38mm/42mm to 42mm/46mm) and displays have expanded to cover more of the front surface. Materials have diversified from the initial aluminum and stainless steel to include titanium, ceramic and various recycled materials as part of Apple’s environmental initiatives.
Inside, each generation has delivered improvements in processing power and efficiency. The S1 chip in the original model has evolved to the S10 System in Package (SiP). Battery life has improved from around 18 hours to over 36 hours on Ultra models. Display technology has progressed from OLED to LTPO3 with variable refresh rates. Water resistance increased from splash protection to a 100-meter depth rating on dive-capable models.
The software experience has similarly evolved through incremental refinements. WatchOS 1’s app-centric interface has given way to more glanceable interactions, complications and the Smart Stack introduced in watchOS 10, which uses machine learning to surface relevant information throughout the day.
As the Apple Watch enters its second decade, deeper health integration through partnerships with healthcare systems, insurers and medical researchers is expanding how Watch data can inform clinical decision-making. Non-invasive sensing capabilities continue to be developed, with persistent rumors pointing to blood glucose monitoring as a target capability.